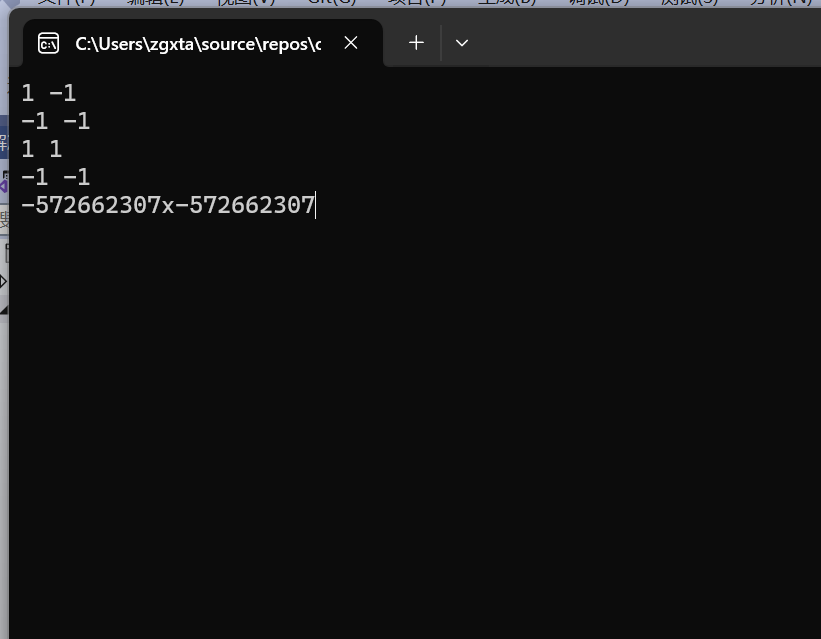
pta上面的一元多项式相加题目,用链表实现遇到了一些问题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int pow;
int cof;
struct Node* next;
};
typedef struct Node* node;
node gettail(node list) {
node tail = list;
while (tail->next != NULL) {
tail = tail->next;
}
return tail;
}
void inserttail(node list, int pow, int cof) {
node tail = gettail(list);
node newtail = new struct Node;
newtail->pow = pow;
newtail->cof = cof;
newtail->next = tail->next;
tail->next = newtail;
}
node createlist() {
node list = new struct Node;
list->next = NULL;
int pow, cof;
while (1) {
cin >> pow >> cof;
if (pow == -1 && cof == -1) {
break;
}
inserttail(list, pow, cof);
}
return list;
}
node delete_zerocof(node list) {
node dummy = new struct Node;
dummy->next = list;
while (dummy->next != NULL) {
if (dummy->next->cof == 0) {
node deleted = dummy->next;
dummy->next = deleted->next;
free(deleted);
}
else {
dummy = dummy->next;
}
}
if (list == NULL) {
node zero = new struct Node;
zero->cof = 0;
zero->pow = 0;
zero->next = list;
return zero;
}
else {
return list;
}
}
node addcof(node list) {
node p = list;
while (p->next != NULL) {
if (p->next->pow == p->pow) {
node deleted = p->next;
p->cof += deleted->cof;
p->next = deleted->next;
free(deleted);
}
else {
p = p->next;
}
}
node LIST=delete_zerocof(list);
return LIST;
}
node merge(node list1, node list2) {
node list = new struct Node;
node dummy = list;
node L1 = list1->next;
node L2 = list2->next;
while (L1 != NULL && L2 != NULL) {
if (L1->pow > L2->pow) {
list->next = L1;
L1 = L1->next;
}
else {
list->next = L2;
L2 = L2->next;
}
list = list->next;
}
if (L1 != NULL) {
list->next = L1;
}
else if (L2 != NULL) {
list->next = L2;
}
return addcof(dummy->next);
}
void showpure(node list) {
node p = list;
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->cof << "x" << p->pow << " ";
p = p->next;
}
}
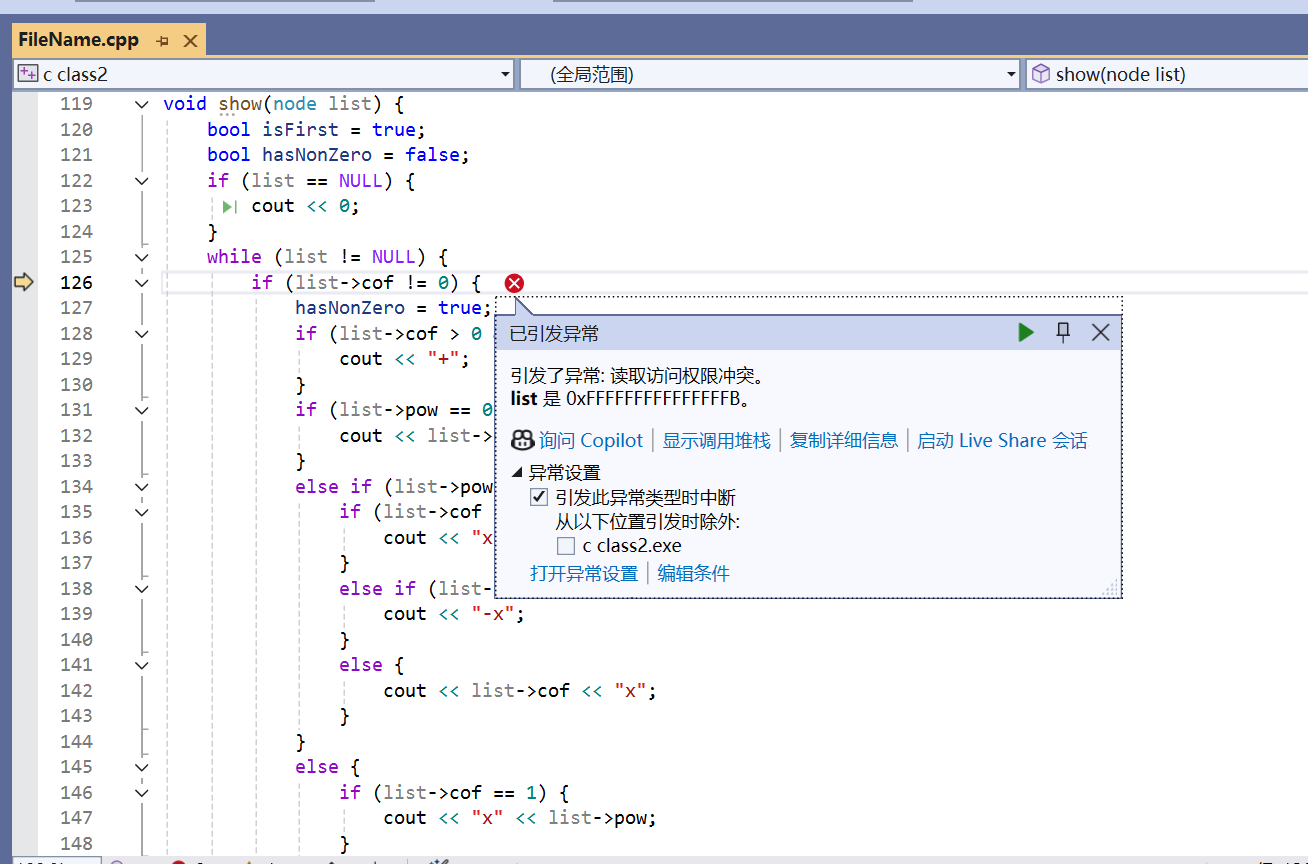
void show(node list) {
bool isFirst = true;
bool hasNonZero = false;
if (list == NULL) {
cout << 0;
}
while (list != NULL) {
if (list->cof != 0) {
hasNonZero = true;
if (list->cof > 0 && !isFirst) {
cout << "+";
}
if (list->pow == 0) {
cout << list->cof;
}
else if (list->pow == 1) {
if (list->cof == 1) {
cout << "x";
}
else if (list->cof == -1) {
cout << "-x";
}
else {
cout << list->cof << "x";
}
}
else {
if (list->cof == 1) {
cout << "x" << list->pow;
}
else if (list->cof == -1) {
cout << "-x" << list->pow;
}
else {
cout << list->cof << "x" << list->pow;
}
}
}
isFirst = false;
list = list->next;
}
if (!hasNonZero) {
cout << "0";
}
}
int main()
{
node list1 = createlist();
node list2 = createlist();
node list = merge(list1, list2);
show(list);
//showpure(list);
return 0;
}

