上午好☀️☀️☀️️
本答案参考通义千问
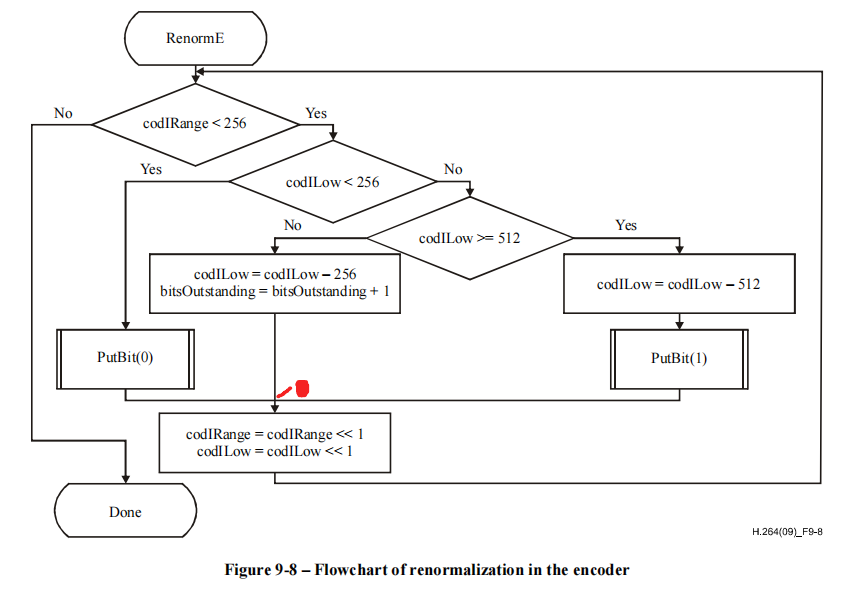
在 H.264 标准中,CABAC(Context-Based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding) 是一种高效的熵编码方法,用于压缩视频数据。你提到的“交叉点”问题,实际上涉及 CABAC 编码过程中 bit 位的输出逻辑 和 状态转移 的关键部分。
✅ 一、“交叉点”的定义与理解
在你描述的场景中,PutBit(0) 或 PutBit(1) 是将一个二进制位写入输出缓冲区的操作,而随后进行的是:
codIRange = codIRange << 1;
codILow = codILow << 1;
这表示当前编码状态(codIRange 和 codILow)被左移一位,相当于对当前上下文进行更新,进入下一轮的编码循环。
这个“十字交叉点”确实是 CABAC 编码中的一个重要“状态转移点”,即从当前编码状态转移到下一状态的边界点。
✅ 二、理论依据:H.264 标准文档《T-REC-H.264-201106》
根据 ITU-T H.264 标准文档(《T-REC-H.264-201106-T!!PDF-E.pdf》),特别是 第 9 章:Entropy coding 部分,明确描述了 CABAC 的工作流程。
重点摘录(第 9.3.1 节):
“The binary arithmetic coder is used for the encoding of the bit stream. The context model and the arithmetic coding process are described in this section. The binary arithmetic coder operates by maintaining a range (codIRange) and a low value (codILow).”
“After each bit is encoded, the range and low values are updated by shifting left by one bit, and the corresponding bits are written to the output buffer.”
“This process continues until all bits have been encoded or the range becomes zero.”
✅ 三、CABAC 编码流程的详细步骤(有序列表)
以下是 CABAC 编码的基本流程,其中包含了你提到的“交叉点”逻辑:
-
初始化:
codIRange = 2^15(或根据上下文确定)codILow = 0bitsOutstanding = 0
-
判断当前编码状态:
- 如果
codIRange < 2^14,则需要进行 renormalization(归一化),即将 codIRange 和 codILow 左移,并输出对应的位。
-
决定当前位是 0 还是 1:
- 基于当前上下文模型的概率,选择
PutBit(0) 或 PutBit(1)。
-
执行位输出:
-
再次检查是否需要归一化:
- 如果
codIRange < 2^14,继续归一化处理。
-
重复上述过程直到所有 bit 编码完成。
✅ 四、“交叉点”是否为状态转移点?
是的,“交叉点”就是状态转移点,具体体现在以下两个方面:
- 逻辑上:
PutBit(0) 或 PutBit(1) 后,进入下一个编码状态(通过左移操作)。 - 结构上:这是 CABAC 编码中 状态机 的一个关键跳转点,标志着当前 bit 编码完成,进入下一轮编码。
✅ 五、代码示例(修改后的 CABAC 伪代码)
下面是简化版的 CABAC 编码伪代码,展示了“交叉点”的逻辑:
// 初始化
codIRange = 2^15;
codILow = 0;
bitsOutstanding = 0;
while (还有 bit 需要编码) {
// 检查是否需要归一化
while (codIRange < 2^14) {
PutBit((codILow >> 14) & 1); // 输出当前最高位
codILow = (codILow << 1) & 0x3FFFFFFF; // 左移并截断
codIRange = codIRange << 1;
bitsOutstanding++;
}
// 选择当前 bit 是 0 还是 1
if (context_model predicts 0) {
PutBit(0);
codILow = codILow - codIRange;
} else {
PutBit(1);
}
// 状态转移:左移 codILow 和 codIRange
codIRange = codIRange << 1;
codILow = codILow << 1;
// 更新上下文模型
update_context_model();
}
注意:此代码为简化版本,实际实现中还需考虑归一化和上下文模型更新等细节。
✅ 六、结论总结
| 项目 | 内容 |
|------|------|
| 是否为交叉点 | ✅ 是,是 CABAC 编码中的状态转移点 |
| 理论依据 | 《T-REC-H.264-201106》第 9 章:Entropy coding |
| 关键操作 | PutBit() → codILow << 1 和 codIRange << 1 |
| 意义 | 表示当前 bit 编码完成,进入下一轮编码 |
如需进一步了解 CABAC 的上下文建模、概率估计、归一化机制等,可参考标准文档第 9.3.1 至 9.3.3 小节。