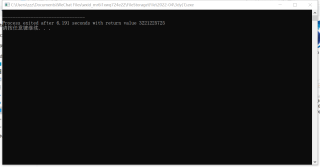
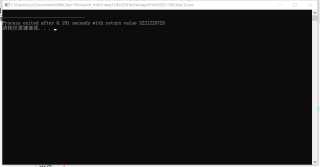
X[100000], Y[100000], fx, C[1000000],局部变量的数组长度太大了
函数内局部变量的数组长度不能太大
把数组定义放在 main()函数外面改成全局变量的数组即可.
或者用 malloc()动态分配内存空间
局部变量是在程序运行栈上自动分配的,一般运行栈的大小是比较小的,大约即1~2MB,如果你定义一个很大的局部变量,很可能导致栈溢出。
而全局变量是在数据段中在程序加载时自动分配,大小可以定义的很大,只要你的电脑内存足够大。
你题目的解答代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
double LagrangeInterPol(double arrX[], double arrY[], int n, double x);
double NewtonInterPol(double arrX[], double arrY[], int n, double x);
double Polyfit(double arrX[], double arrY[], int order, int n, double x, double Coeffi[]);
void printout(double x,double n,int e);
double maingauss(int n, double A[][1000], double X[]);
using namespace std;
double X[100000], Y[100000], fx, C[1000000]; //把数组定义放在 main()函数外面改成全局变量的数组即可.
int main()
{
int k=0,o=0,n=0;
double x1,x2,x3;
cout <<"请选择算法:1、拉格朗日,2、牛顿,3、最小二乘";
cin >> k;
if(k==1)
{
cout << "请输入阶数";
cin >> n;
n = n + 1;
cout <<"请输入要求的点的个数";
cin >>o;
for(int j=0;j<o;j++)
{
cout << "请输入所要求的点";
cin >> fx;
cout << "请输入x,y的值:";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> X[i] >> Y[i];
}
x1=LagrangeInterPol(X, Y, n, fx);
printout(x1, fx, 1);
}
}
else if(k==2)
{
cout << "请输入阶数";
cin >> n;
n = n + 1;
cout <<"请输入要求的点的个数";
cin >>o;
for(int j=0;j<o;j++)
{
cout << "请输入所要求的点";
cin >> fx;
cout << "请输入x,y的值:";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> X[i] >> Y[i];
}
x2=NewtonInterPol(X, Y, n, fx);
printout(x2, fx, 2);
}
}
else if(k==3)
{
cout << "请输入阶数";
cin >> n;
n = n + 1;
cout <<"请输入要求的点的个数";
cin >>o;
for(int j=0;j<o;j++)
{
cout << "请输入所要求的点";
cin >> fx;
cout << "请输入x,y的值:";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> X[i] >> Y[i];
}
x3=Polyfit(X, Y, n - 1, n,fx, C);
printout(x3, fx, 3);
}
}
else
{
cout <<"输入错误";
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
double LagrangeInterPol(double arrX[], double arrY[], int n, double x)
{
double l = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double s = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (i != j)
{
s *= (x - arrX[j]) / (arrX[i] - arrX[j]);
}
}
l += arrY[i] * s;
}
return l;
}
void printout(double x, double n, int e)
{
if (e == 1)
{
cout << "拉格朗日插值f(" << n << ") = " << x<<endl;
}
else if (e == 2)
{
cout << "牛顿插值f(" << n << ") = " << x << endl;
}
else if (e == 3)
{
cout <<"最小二乘法f(" << n << ") = " << x << endl;
}
}
double NewtonInterPol(double arrX[], double arrY[], int n, double x)
{
double cs[n][n],l=0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cs[i][0] = arrY[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j < n; j++)
{
cs[i][j] = (cs[i][j - 1] - cs[i - 1][j - 1]) / (arrX[j] - arrX[0]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double s = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
s *= (x - arrX[j]);
}
l += cs[i][i] * s;
}
return l;
}
double Polyfit(double arrX[], double arrY[], int order, int n, double x, double Coeffi[])
{
double A[order+1][1000];
A[0][0] = n;
double m[2 * order];
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * order; i++)
{
double l = 1;
double s = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
l *= arrX[j];
}
s += l;
}
m[i] = s;
}
for (int i = 0; i < order + 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < order + 1; i++)
{
if (i == j == 0)
{
j++;
}
A[i][j] = m[i + j - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <order+1; i++)
{
double l = 1;
double s = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
l *= arrX[j];
}
s += l * arrY[j];
}
A[i][order+1] = s;
}
maingauss(order, A, Coeffi);
double fx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < order + 1; i++)
{
double l = 1;
double s = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < order + 1; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
l *= x;
}
s += l * Coeffi[j];
}
fx += s;
}
return fx;
}
double maingauss(int n, double A[][1000], double X[])//高斯列主元消元法
{
int i, j, k, c;
double D[n][1000], Q[n];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < n + 1; j++)
{
D[i][j] = A[i][j];
}
}
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
{
int z = c;
for (int l = 0; l < n + 1; l++)
{
Q[l] = D[c][l];
}
for (int d = c; d < n; d++)
{
if (fabs(D[z][c]) < fabs(D[d][c]))
{
for (int m = 0; m < n + 1; m++)
{
Q[m] = D[d][m];
z = d;
}
}
}
for (int v = 0; v < n + 1; v++)
{
D[z][v] = D[c][v];
D[c][v] = Q[v];
}
for (i = c; i < n; i++)
{
k = i + 1;
double b = -D[k][c] / D[c][c];
for (j = c; j < n + 1; j++)
{
D[k][j] += b * D[c][j];
}
}
}
double E[n];
for (int f = 0; f < n; f++)
{
E[f] = D[f][n];
}
X[n - 1] = E[n - 1] / D[n - 1][n - 1];
for (i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
double s = 0;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
s += D[i][j] * X[j];
}
X[i] = (E[i] - s) / D[i][i];
}
return 0;
}
如有帮助,请点击我的回答下方的【采纳该答案】按钮帮忙采纳下,谢谢!