#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
struct state
{
//1表示存在,0表示不在
int exi_man;
int exi_sheep;
int exi_wolf;
int exi_veget;
state(){}
state(int a,int b,int c,int d)
{
exi_man = a;
exi_sheep = b;
exi_wolf = c;
exi_veget = d;
}
bool operator==(state a)
{
return a.exi_man == exi_man && a.exi_sheep == exi_sheep && a.exi_veget == exi_veget && a.exi_wolf == exi_wolf;
}
void print_state()
{
if (exi_man) cout << "人";
if (exi_sheep) cout << "羊";
if (exi_wolf) cout << "狼";
if (exi_veget) cout << "菜";
}
bool check_state()
{
bool temp= (exi_man == 0 && exi_sheep == 1 && exi_wolf == 1 && exi_veget == 1)
|| (exi_man == 1 && exi_sheep == 0 && exi_wolf == 0 && exi_veget == 0)
|| (exi_man == 0 && exi_sheep == 1 && exi_wolf == 0 && exi_veget == 1)
|| (exi_man == 1 && exi_sheep == 0 && exi_wolf == 1 && exi_veget == 0)
|| (exi_man == 0 && exi_sheep == 1 && exi_wolf == 1 && exi_veget == 0)
|| (exi_man == 1 && exi_sheep == 0 && exi_wolf == 0 && exi_veget == 1);
return !temp;
}
void move_in(state a)//这里的a只带入choice[i]
{
exi_man += a.exi_man;
exi_sheep += a.exi_sheep;
exi_wolf += a.exi_wolf;
exi_veget += a.exi_veget;
}
void move_out(state a)//这里的a只带入choice[i]
{
exi_man -= a.exi_man;
exi_sheep -= a.exi_sheep;
exi_wolf -= a.exi_wolf;
exi_veget -= a.exi_veget;
}
}_state(1,1,1,1);
//共有4种决策:啥也不带,带羊,带狼,带菜
state choice[4] = { {1,0,0,0} ,{1,1,0,0}, {1,0,1,0},{1,0,0,1} };
//如果决策正确,会用以记录决策号
int record[100] = { -1 };
void print_choice(state a)
{
if (a == choice[0]) cout << "空气 ";
if (a == choice[1]) cout << "羊 ";
if (a == choice[2]) cout << "狼 ";
if (a == choice[3]) cout << "菜 ";
}
int main()
{
int num_step = 0;
while (true)
{
state temp = _state;
if (num_step % 2 == 0)
{
int i = 0;
flag1:
cout << i << endl;
temp = _state;
temp.move_out(choice[i]);
if (temp.check_state()) {
record[num_step] = i;
_state = temp;
goto flag;
}
i++;
goto flag1;
}
else
{
int i = 0;
flag2:
cout << i << endl;
temp = _state;
temp.move_in(choice[i]);
if (temp.check_state()) {
record[num_step] = i;
_state = temp;
goto flag;
}
i++;
goto flag2;
}
flag:
num_step++;
if (_state.exi_man == 0 && _state.exi_sheep == 0 && _state.exi_wolf == 0 && _state.exi_veget == 0)
{
cout << "共计:" << num_step << "步" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num_step; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0){
cout << "船夫带走了";
print_choice(choice[i]);
cout << endl;
}
else {
cout << "船夫带回了";
print_choice(choice[i]);
cout << endl;
}
cout << "搬运成功!" << endl;
system("pause");
}
break;
}
}
}(C++::狼羊菜过河问题)我的程序哪里错了?
- 写回答
- 好问题 0 提建议
- 关注问题
- 邀请回答
-
2条回答 默认 最新
 upc_hxc 2021-03-13 00:11关注
upc_hxc 2021-03-13 00:11关注【结论】:从第三步(即第二次执行第1个循环)开始错
【分析】:此时的状态为左岸(起始地)为狼和菜,右岸(目的地)为农夫和羊,如下图(b)所示。在执行第三步时,先选择choice[0](1,0,0,0),即农夫回到左岸,如下图(c)所示,满足判断条件。再执行第四步时,同样先选择choice[0](1,0,0,0),即农夫又到右岸,如下图(b)所示。综上,再后续的代码中,始终进行choice[0]后可以满足“安全”的判断条件,但是不满足最终的判断条件,所以就在图(b)和图(c)的状态之间无限循环。而选择也始终是choice[0],所以打印的i也始终是0。
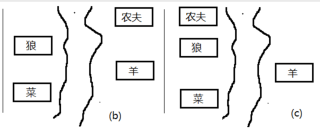
【解决方案】:1、不能让同一种选择在相邻的两个步骤中出现,例如:第一步选择choice[1]{1,1,0,0}带羊,第二步不能再选择choice[1]{1,1,0,0}带羊,否则就同样陷入死循环:把羊来过去又带过来。所以可以引入一个变量记录每一步的选择,则下一步跳过该选择;
2、在做任何选择后,任何物种的数量都只能是1和0,需要在每一步做判断,或者直接用布尔值;
【题外话】1、强烈建议不要使用goto,宁可多花时间思考更复杂的循环,百益而无一害;
2、题主的代码在最后调用print_choice()时,传入的参数也有问题,可以自行看一下。
本回答被题主选为最佳回答 , 对您是否有帮助呢?解决 无用评论 打赏 举报
