
数字图像处理,如何准确计数火柴的数量,而不受火柴交叉的干扰,
现有思路有直线检测,轮廓检测,都无法实现,该怎么处理
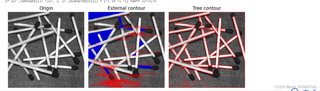
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 12.2 绘制轮廓
img = cv2.imread("/content/matches-random.tif", flags=1)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 灰度图像
_, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_OTSU + cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
# 12.3 绘制原始图像
plt.subplot(131), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("Origin")
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 12.4 寻找二值化图中的轮廓
if cv2.__version__.startswith('3'):
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # OpenCV3
else:
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # OpenCV4~
# 12.5 绘制最内层轮廓
contourEx = img.copy()
for i in range(len(contours)):
if hierarchy[0][i][2] == -1:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[i])
text = "{}({},{})".format(i, x, y)
contourEx = cv2.drawContours(contourEx, contours, i, (205, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
contourEx = cv2.putText(contourEx, text, (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255))
print("i=", i, ",contours[i]:", contours[i].shape, ",hierarchy[0][i] =", hierarchy[0][i], "text=", text)
# 12.6 绘制全部轮廓
contourTree = img.copy()
contourTree = cv2.drawContours(contourTree, contours, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 12.7 显示绘制结果
plt.subplot(132), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("External contour")
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(contourEx, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.subplot(133), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("Tree contour")
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(contourTree, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

