我想使用ALBERT和孪生网络来训练一个主观问题评分模型,孪生网络由双向LSTM和全连接层组成。在训练中,我注意到准确性并没有提高,一直保持不变。我感觉像是权重没有更新,可能是因为梯度太小导致了权重变化不大。或者,训练策略可能存在问题,但我不确定具体原因。下面是我训练期时的准确性:
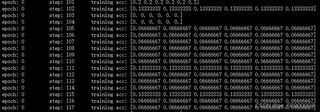
下面是我训练的代码:
class MetaTask(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, args):
super(MetaTask, self).__init__()
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
self.update_lr = args.update_lr
self.meta_lr = args.meta_lr
self.finetunning_lr = args.finetunning_lr
self.n_way = args.n_way
self.k_spt = args.k_spt
self.k_qry = args.k_qry
self.task_num = args.task_num
self.update_step = args.update_step
self.update_step_test = args.update_step_test
self.net = SubjectiveGradingModel().to(self.device)
self.meta_optim = optim.Adam(self.net.parameters(), lr=self.meta_lr)
def forward(self, support_x, support_y, query_x, query_y):
task_num = len(support_x)
querysz = len(query_x[0])
losses_q = [0 for _ in range(self.update_step + 1)]
corrects = [0 for _ in range(self.update_step + 1)]
for i in range(task_num):
self.net.train()
# 1. run the i-th task and compute loss for k=0
logits = self.net(support_x[i])
loss = self.loss_fn(logits, torch.cat(support_y[i], dim=0).long())
fast_weights = OrderedDict(self.net.named_parameters())
grad = torch.autograd.grad(loss, fast_weights.values(), retain_graph=True)
# 输出梯度为None的参数
# for (name, param), gra in zip(self.net.named_parameters(), grad):
# if gra is None:
# print("梯度为None的参数:", name)
fast_weights = OrderedDict(
(name, param - self.update_lr * grad)
for ((name, param), grad) in zip(fast_weights.items(), grad)
)
# this is the loss and accuracy before first update
with torch.no_grad():
self.net.eval()
logits_q = self.net(query_x[i])
loss_q = self.loss_fn(logits_q, torch.cat(query_y[i], dim=0).long())
losses_q[0] += loss_q
pred_q = F.softmax(logits_q, dim=1).argmax(dim=1)
correct = torch.eq(pred_q, torch.cat(query_y[i], dim=0).long()).sum().item()
corrects[0] = corrects[0] + correct
# this is the loss and accuracy after the first update
with torch.no_grad():
self.net.eval()
self.net.load_state_dict(fast_weights, strict=False)
logits_q = self.net(query_x[i])
loss_q = self.loss_fn(logits_q, torch.cat(query_y[i], dim=0).long())
losses_q[1] += loss_q
pred_q = F.softmax(logits_q, dim=1).argmax(dim=1)
correct = torch.eq(pred_q, torch.cat(query_y[i], dim=0).long()).sum().item()
corrects[1] = corrects[1] + correct
self.net.train()
for k in range(1, self.update_step):
# 1. run the i-th task and compute loss for k=1~K-1
self.net.load_state_dict(fast_weights, strict=False)
logits = self.net(support_x[i])
loss = self.loss_fn(logits, torch.cat(support_y[i], dim=0).long())
# 2. compute grad on theta_pi
fast_weights = OrderedDict(self.net.named_parameters())
grad = torch.autograd.grad(loss, fast_weights.values(), retain_graph=True)
# 3. theta_pi = theta_pi - train_lr * grad
fast_weights = OrderedDict(
(name, param - self.update_lr * grad)
for ((name, param), grad) in zip(fast_weights.items(), grad)
)
self.net.load_state_dict(fast_weights, strict=False)
logits_q = self.net(query_x[i])
# loss_q will be overwritten and just keep the loss_q on last update step.
loss_q = self.loss_fn(logits_q, torch.cat(query_y[i], dim=0).long())
losses_q[k + 1] += loss_q
with torch.no_grad():
pred_q = F.softmax(logits_q, dim=1).argmax(dim=1)
correct = torch.eq(pred_q, torch.cat(query_y[i], dim=0).long()).sum().item() # convert to numpy
corrects[k + 1] = corrects[k + 1] + correct
loss_q = losses_q[-1] / task_num
# optimize theta parameters
self.meta_optim.zero_grad()
loss_q.backward(retain_graph=True)
# print('meta update')
self.meta_optim.step()
accs = np.array(corrects) / (querysz * task_num)
return accs
class SubjectiveGradingModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size=384):
super(SubjectiveGradingModel, self).__init__()
# 加载预训练的BERT模型和分词器
self.bert = AlbertModel.from_pretrained('src/datamoudle/model/albert_chinese_small')
# 孪生网络
self.siamese_network = Siamese(max_length=378, embedding_size=hidden_size)
def forward(self, input_data ,weights=None):
# 将每个字典中的数据拆分成单独的列表
input_ids_list = [item['input_ids'].squeeze(0).squeeze(0) for item in input_data]
token_type_ids_list = [item['token_type_ids'].squeeze(0).squeeze(0) for item in input_data]
attention_mask_list = [item['attention_mask'].squeeze(0).squeeze(0) for item in input_data]
answer_input_ids_list = [item['answer_input_ids'].squeeze(0).squeeze(0) for item in input_data]
answer_token_type_ids_list = [item['answer_token_type_ids'].squeeze(0).squeeze(0) for item in input_data]
answer_attention_mask_list = [item['answer_attention_mask'].squeeze(0).squeeze(0) for item in input_data]
# 转换成 PyTorch 张量
input_ids = torch.stack(input_ids_list)
token_type_ids = torch.stack(token_type_ids_list)
attention_mask = torch.stack(attention_mask_list)
answer_input_ids = torch.stack(answer_input_ids_list)
answer_token_type_ids = torch.stack(answer_token_type_ids_list)
answer_attention_mask = torch.stack(answer_attention_mask_list)
outputs = self.bert(input_ids=input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
pooled_output = outputs.last_hidden_state
cls_output = outputs.pooler_output
outputs_answer = self.bert(input_ids=answer_input_ids, token_type_ids=answer_token_type_ids, attention_mask=answer_attention_mask)
pooled_output_answer = outputs_answer.last_hidden_state
cls_output_answer = outputs_answer.pooler_output
siamese_output = self.siamese_network(pooled_output, pooled_output_answer, cls_output, cls_output_answer)
return siamese_output
class LSTMEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embed_size, hidden_size, num_layers, bidir, dropout):
super(LSTMEncoder, self).__init__()
self.embed_size = embed_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.bidir = bidir
if self.bidir:
self.direction = 2
else: self.direction = 1
self.dropout = dropout
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=self.embed_size, hidden_size=self.hidden_size, dropout=self.dropout,
num_layers=self.num_layers, bidirectional=self.bidir)
def initHiddenCell(self, batch_size):
rand_hidden = Variable(torch.randn(self.direction * self.num_layers, batch_size, self.hidden_size, requires_grad=True)).to(self.device)
rand_cell = Variable(torch.randn(self.direction * self.num_layers, batch_size, self.hidden_size, requires_grad=True)).to(self.device)
return rand_hidden, rand_cell
def forward(self, input, hidden, cell):
output, (hidden, cell) = self.lstm(input, (hidden, cell))
return output, hidden, cell
class Siamese(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, max_length, embedding_size):
super(Siamese, self).__init__()
self.max_length = max_length
# 定义第一个 LSTM 编码器
self.encoder = LSTMEncoder(embed_size=embedding_size, hidden_size=64, num_layers=1, bidir=True,dropout=0.2)
self.input_dim = 5 * self.encoder.direction * self.encoder.hidden_size
# 定义一个 classifier 层序列
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(896, self.input_dim // 2),
nn.Linear(self.input_dim // 2, 9)
)
def forward(self, student_answer_emb, model_answer_emb, v1, v2):
#model_answer_support = model_answer_emb.repeat(student_answer_emb.size(0), 1, 1)
# 取BERT输出的CLS token作为表示
# v1 = student_answer_emb[:, 0, :]
# v2 = model_answer_emb[:, 0, :]
# 初始化LSTM的隐藏状态和细胞状态
h1, c1 = self.encoder.initHiddenCell(batch_size=student_answer_emb.size(0))
h2, c2 = self.encoder.initHiddenCell(batch_size=model_answer_emb.size(0))
# 使用LSTM编码器获取序列表示
_, h1, c1 = self.encoder(student_answer_emb.permute(1, 0, 2), h1, c1)
_, h2, c2 = self.encoder(model_answer_emb.permute(1, 0, 2), h2, c2)
# 取LSTM编码的最后一个时间步的隐藏状态作为表示
lstm_v1 = h1[-1, :, :]
lstm_v2 = h2[-1, :, :]
# 利用这两个编码向量
features = torch.cat((v1, v2, lstm_v1, lstm_v2), 1)
# 输入特征到分类器
output = self.classifier(features)
output = F.softmax(output, dim=1)
return output

